Some computer users are still using Windows XP on their computers as people just love this operating system. Therefore, we have a series of tutorials to help die-hard Windows XP fans navigate and use their operating system. Below we have a detailed tutorial about how you can add, change, or remove programs in Windows XP and Windows 11. Sometimes you might choose to remove a program or maybe your program is playing up and clashing with other applications on your system. You might need to force quit your program to shut it down, then either repair it or remove it. Either way, knowing how to remove and change programs correctly is a benefit to you.
In Windows Vista and Seven, you can remove programs from your computer pretty much the same way. Of course, it looks different, and a few names have changed, but don’t let that fool you. Just be sure you know what programs and files are safe to delete before doing anything drastic!
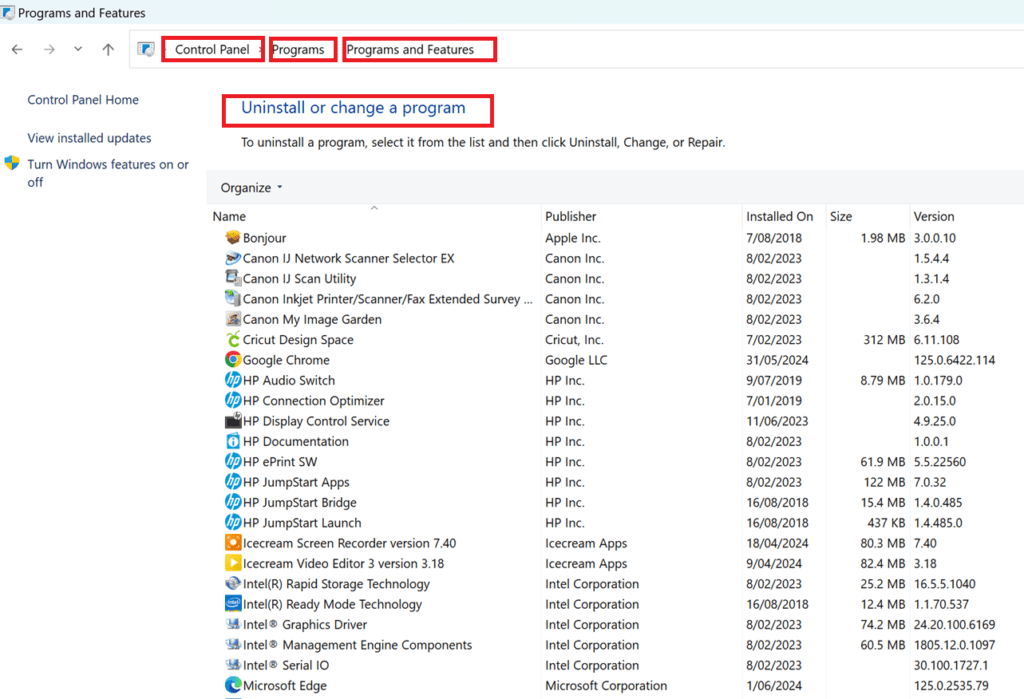
Add or Remove Windows Programs
For Windows XP
- Click Start:
- Begin by clicking on the Start menu at the bottom left corner of your screen.
- Go to Control Panel:
- Navigate to the Control Panel and click on it.
- Open Add or Remove Programs:
- Within the Control Panel, find and click on “Add or Remove Programs.” This will open the Add or Remove Programs window, displaying a list of currently installed programs.
Viewing Installed Updates
- Show Updates:
- If you would like to see updates installed on your machine, tick the box labeled “Show Updates.” This will list all of the updates installed on your system.
Changing or Removing a Program
- Select the Program:
- Locate the program you wish to change or remove from the list.
- Click the button corresponding to the program. Ensure you have selected the correct program, as some may not prompt you to confirm before removal.
- Confirm Changes:
- Follow the prompts to change or remove the program. Be cautious as this action might not always ask for confirmation.
Adding or Removing Windows Components
- Access Windows Components:
- In the Add or Remove Programs window, find the option to “Add/Remove Windows Components.”
- Select Components:
- A list of all available Windows components will appear. You can select or deselect components to add or remove them.
- Example:
- To remove Windows Messenger, uncheck the option next to it, click Next, and Windows will configure the changes.
- To add Windows Messenger back, check the option, click Next, and it will be reinstalled.
- Finish Configuration:
- Click Finish when you’re done making changes.
Watch this old ancient video tutorial removing programs in Windows XP.
For Windows 11
Step-by-Step Guide
- Open Settings:
- Click on the Start menu and select Settings (gear icon), or press
Win + Ito open the Settings directly.
- Click on the Start menu and select Settings (gear icon), or press
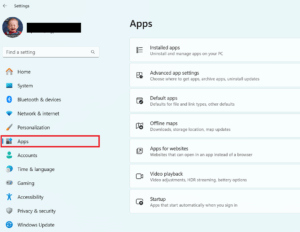
- Navigate to Apps:
- In the Settings window, click on the “Apps” category from the left sidebar.
- Open Apps & Features:
- Click on “Apps & Features” in the main pane. This will display a list of all installed apps and features on your computer.
Adding or Removing a Program
- Locate the Program:
- Scroll through the list to find the program you want to remove.
- Uninstall the Program:
- Click on the three vertical dots next to the program name and select “Uninstall.”
- Follow the prompts to complete the uninstallation.
- Add a New Program:
- To install a new program, download the installer from a trusted source.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Viewing and Managing Optional Features
- Manage Optional Features:
- In the “Apps & Features” section, click on “Optional features” to manage additional Windows components.
- Click “Add a feature” to install new components or select existing ones to remove.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have demonstrated how to add, remove, or change programs and Windows components in both Windows XP and Windows 11. These steps are essential for maintaining and managing your system effectively. Always proceed with caution when removing programs to avoid unintended consequences.