A path to a folder directory or file is a string of folder names that indicate where a particular file is located on your computer. For example, the true path to the “My Pictures” folder might be C:\Documents and Settings\YourUserName\My Documents\My Pictures. While Windows provides shortcuts to commonly used folders in the Start menu, finding paths to other files and folders can be more challenging.
This tutorial not only covers Windows XP, but if you’re using Windows Vista, Windows 7, or a newer version, sometimes you need to follow different steps to find a folder path.
In Windows XP, the path to a file or folder is automatically displayed in the address bar at the top of the window when you navigate to it. To locate the file path of documents and images, simply browse through your computer’s folders to find their locations.
What is a Directory and What is a Folder?
Before we proceed, let’s clarify some terminology. You might hear the terms “directory” and “folder” used interchangeably, and that’s perfectly fine. Here’s why:
In the early days of computing, before graphical interfaces like Windows were developed, the term “directory” was commonly used. A directory is a way to organize and store files on a computer. It was purely text-based and used in command-line interfaces to navigate the file system.
With the advent of Windows and its graphical user interface, directories began to be represented visually as “folders.” Windows 3.1, one of the earliest versions, displayed directories as icons resembling manila folders on the screen. This visual representation made it easier for users to understand and navigate their file systems.
So, whether you call it a “folder” or a “directory,” you’re referring to the same thing. A directory is a place where files are stored, and a folder is simply the graphical representation of that directory. It’s perfectly acceptable to use either term, or even “directory folder,” to describe this basic organizational unit in your computer’s file system.
What is the Difference Between a Folder Path and a File Path?
A folder (or directory) is a container used to store files, which can be anything from pictures to word documents. The path to a folder is essentially its address on your computer, indicating where the folder is located within the file system. Similarly, the path to a file is the specific address where that file is stored on your computer. In summary:
- Folder Path: The address where a folder is kept on your computer.
- File Path: The address where a specific file is kept within a folder on your computer.
Instructions for Finding Folder and File Paths in Various Windows Versions
Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Find Folder Path:
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Win + E. - Navigate to the folder you want to find the path for.
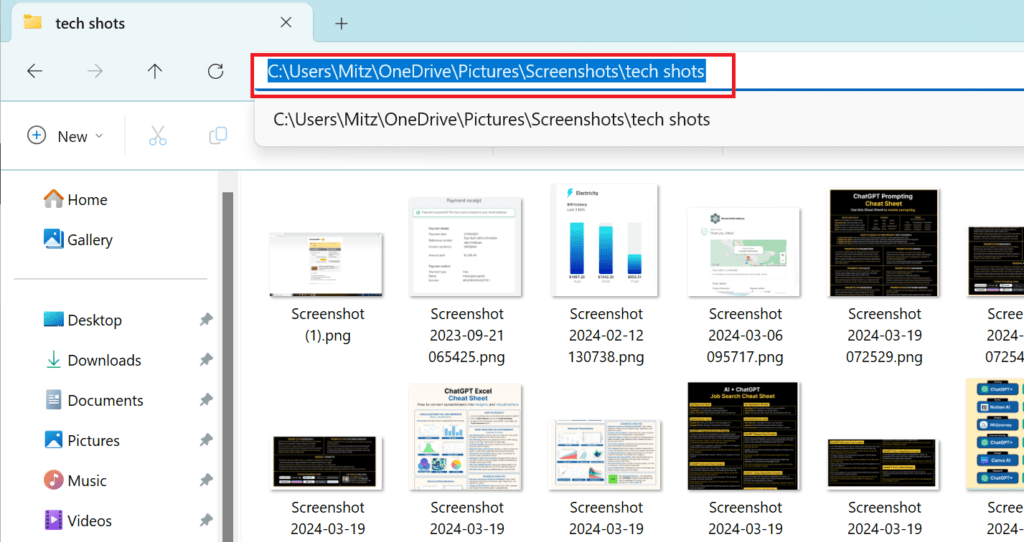
- Click on the address bar at the top. The full path will be highlighted.
- Press
Ctrl + Cto copy the path.
- Open File Explorer by pressing
- Find File Path:
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Win + E. - Navigate to the file you want to find the path for.
- Right-click the file and select “Properties.”
- In the “General” tab, look for the “Location” field. This shows the folder path.
- Combine the “Location” with the file name to get the full file path.
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Windows 8.1
- Find Folder Path:
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Win + E. - Navigate to the folder you want to find the path for.
- Click on the address bar at the top. The full path will be highlighted.
- Press
Ctrl + Cto copy the path.
- Open File Explorer by pressing
- Find File Path:
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Win + E. - Navigate to the file you want to find the path for.
- Right-click the file and select “Properties.”
- In the “General” tab, look for the “Location” field. This shows the folder path.
- Combine the “Location” with the file name to get the full file path.
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Windows 7
- Find Folder Path:
- Open Windows Explorer by clicking on the folder icon in the taskbar.
- Navigate to the folder you want to find the path for.
- Click on the address bar at the top. The full path will be highlighted.
- Press
Ctrl + Cto copy the path.
- Find File Path:
- Open Windows Explorer by clicking on the folder icon in the taskbar.
- Navigate to the file you want to find the path for.
- Right-click the file and select “Properties.”
- In the “General” tab, look for the “Location” field. This shows the folder path.
- Combine the “Location” with the file name to get the full file path.
Windows XP
- Find Folder Path:
- Open Windows Explorer by clicking on the “Start” button and selecting “My Computer.”
- Navigate to the folder you want to find the path for.
- The full path will be shown in the address bar at the top.
- Press
Ctrl + Cto copy the path.
- Find File Path:
- Open Windows Explorer by clicking on the “Start” button and selecting “My Computer.”
- Navigate to the file you want to find the path for.
- Right-click the file and select “Properties.”
- In the “General” tab, look for the “Location” field. This shows the folder path.
- Combine the “Location” with the file name to get the full file path.
By following these steps, you can easily find the paths to folders and files on your computer, regardless of which version of Windows you are using.
How to Copy a File Path or Folder Path
- Locate the Path:
- Navigate to the file or folder you want to copy the path for.
- Select the Path:
- Click on the address bar at the top of the File Explorer window to highlight the full path. The path will turn blue when selected.
- Copy the Path:
- Right-click on the highlighted (blue) path.
- From the context menu that appears, select “Copy.”
- Paste the Path:
- You can now paste the copied path wherever you need it. For example, to paste it into a Notepad document:
- Open Notepad.
- Right-click in the blank space of the Notepad window.
- Select “Paste” from the context menu.
- You can now paste the copied path wherever you need it. For example, to paste it into a Notepad document:
Example: Accessing Hidden Files
If you need to navigate to files in a hidden folder, you must first enable the option to show hidden files and folders in Windows. Here’s how:
- Show Hidden Files:
- Open File Explorer.
- Click on the “View” tab at the top.
- Check the box for “Hidden items.”
Once hidden files and folders are visible, you can navigate to them and copy their paths using the steps above.
Copying Non-Hidden Files and Folders
For regular documents and images, the files are not hidden by default, so you won’t need to enable the “show hidden files” option. Simply navigate to the file or folder, select the path, and copy it as described.
Why You Need to Know the Path to a File or Folder
Understanding the location of your files and folders is essential for several reasons:
- Efficient Backups: Knowing where your files are stored allows you to back up important data more effectively. This ensures that you don’t miss any critical files when creating backups.
- Easy Transfers: When transferring data to a new computer, knowing the file paths makes it simple to move your internet favorites, documents, and other important folders. You can easily copy and paste them to their new locations.
- Troubleshooting Issues: Knowing file paths can help you troubleshoot issues. If a program or system error occurs, you can locate and manage files directly to resolve problems.
- Script and Automation: For those who create scripts or automate tasks, knowing the exact file paths is crucial. This ensures that the scripts run correctly and access the needed files.
- Advanced File Management: When organizing files, having a clear understanding of their paths allows you to manage and categorize them more efficiently. This helps in keeping your system tidy and well-organized.
- Software Configuration: Some software requires you to specify file paths for certain configurations. Knowing the paths ensures you can set up software correctly and efficiently.
- Security and Permissions: Understanding where files are located helps in managing security settings and permissions. You can ensure sensitive data is stored in secure locations and that only authorized users have access.
- Data Recovery: In case of accidental deletion or data loss, knowing the paths to your files can assist in data recovery efforts. You can target specific directories for recovery operations.
- Development and Testing: For developers and testers, knowing file paths is essential for accessing and manipulating files within their projects. It helps in setting up development environments and testing configurations accurately.
Notes on How To Find The Path To Folders And Files
- Explore Your System: Familiarizing yourself with your computer’s file structure is beneficial. Spend some time browsing through your folders to see where different types of files are stored.
- Show Hidden Files: Some directories and files are hidden by default. You can enable the option to view hidden files in your operating system’s settings.
- Learn About File Extensions: Understanding file extensions can also help you identify the types of files and their associated programs.


