When it comes to network security, one of the most overlooked yet critical steps you can take is to disable unused or vulnerable ports on your system. Open ports act like doors into your network—and if the wrong ones are left unguarded, they can be easily exploited by hackers, malware, and automated bots.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through a list of commonly targeted ports and explain which ports to disable to stop hackers from gaining unauthorized access to your computer or network. Whether you’re securing a home PC or managing small business systems, closing these open doors is an essential step toward hardening your firewall, reducing your attack surface, and protecting sensitive data.
Take control of your digital safety by learning which ports to block—and why doing so is a smart, proactive cybersecurity move.
Port 135 (DCOM Remote Procedure Call – RPC)
- Used for: Windows Remote Procedure Call (RPC), which allows applications to communicate.
- Why disable it?
- Often targeted by worms and malware (e.g., Blaster Worm).
- Used in DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks.
- Not needed unless you use remote administration.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block Port 135" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=135
Port 137-139 (NetBIOS over TCP/IP)
- Used for: Windows file sharing on older networks.
- Why disable it?
- Allows remote attackers to query your computer name and shared resources.
- Used by ransomware and brute-force attacks.
- Not needed unless using legacy Windows file sharing.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block Ports 137-139" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=137-139
Port 445 (SMB – Server Message Block)
- Used for: Windows file sharing and network access.
- Why disable it?
- One of the most attacked ports (used in WannaCry and EternalBlue exploits).
- Allows remote execution of commands if compromised.
- Not needed unless you share files on a local network.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block Port 445" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=445
Port 23 (Telnet)
- Used for: Remote login to a computer.
- Why disable it?
- Sends data in plain text, making it easy to intercept passwords.
- Replaced by SSH (Port 22), which is more secure.
- Used by hackers for remote access attacks.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block Port 23" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=23
Port 3389 (Remote Desktop Protocol – RDP)
- Used for: Remote Desktop connections to access a PC remotely.
- Why disable it?
- Common target for brute-force attacks.
- If exposed to the internet, hackers can take control of your system.
- Use a VPN if you need remote access.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block Port 3389" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=3389
Port 20-21 (FTP – File Transfer Protocol)
- Used for: File transfer between computers.
- Why disable it?
- Transmits passwords in plain text (unsecure).
- Frequently attacked by brute-force password hackers.
- Use SFTP (Port 22) instead.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block FTP Ports" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=20-21
Port 1433-1434 (Microsoft SQL Server)
- Used for: Database connections on Microsoft SQL Server.
- Why disable it?
- Attackers target SQL servers to inject malicious queries.
- Not needed unless you run a SQL server.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block SQL Ports" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=1433-1434
Port 3306 (MySQL Database)
- Used for: MySQL database connections.
- Why disable it?
- If open to the internet, attackers can steal or delete databases.
- Use a VPN or firewall rules to restrict access.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block MySQL Port" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=3306
Port 1723 (PPTP VPN)
- Used for: Older VPN connections.
- Why disable it?
- Insecure VPN protocol with known vulnerabilities.
- Use OpenVPN or WireGuard instead.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block PPTP VPN Port" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=1723
Port 5000 (UPnP – Universal Plug and Play)
- Used for: Automatic device discovery on local networks.
- Why disable it?
- Hackers can use UPnP to bypass firewalls.
- Malware can open ports without your knowledge.
- Not needed unless using smart home devices.
- Disable using Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Block UPnP Port" dir=in action=block protocol=TCP localport=5000
Bonus: Block All Unused Ports with Firewall
To block all unused ports, create a default deny rule in Windows Firewall:
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles firewallpolicy blockinbound,allowoutbound
This blocks all incoming traffic unless specifically allowed, while still allowing outbound connections.
How to Test If Ports Are Successfully Blocked
After disabling ports, you need to verify that they are truly blocked. Below are multiple ways to test blocked ports in Windows using built-in tools and external scanners.
1. Check Blocked Ports Using Netstat
The netstat command shows active ports and listening services. See How to Analyze Your Network Connections Using Netstat in Windows
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (
Win + R, typecmd, pressCtrl + Shift + Enter). - Type the following command to check if a port is still open:
netstat -an | findstr :[PORT]Replace[PORT]with the port number you want to check. Example (Checking if Port 445 is blocked):netstat -an | findstr :445- If the port is blocked, there will be no output.
- If the port is still open, you’ll see it in the list (e.g.,
LISTENINGorESTABLISHED).
2. Use PowerShell to Test a Port
PowerShell can check if a port is accepting connections.
Steps:
- Open PowerShell as Administrator (
Win + X, select PowerShell (Admin)). - Run this command:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName localhost -Port [PORT]Replace[PORT]with the number you want to check. Example (Checking if Port 3389 is open):Test-NetConnection -ComputerName localhost -Port 3389- If blocked, the result will show “TcpTestSucceeded: False”.
If still open, it will show “TcpTestSucceeded: True”.
- If blocked, the result will show “TcpTestSucceeded: False”.
3. Use Telnet to Check Port Accessibility
Telnet can test whether a port is accepting connections.
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt (
Win + R, typecmd, press Enter). - Type:
telnet localhost [PORT]Replace[PORT]with the port number you want to check. Example (Checking if Port 23 is open):telnet localhost 23
If blocked, the connection will fail (you’ll see “Could not open connection”).
If open, the screen will go blank, meaning the port is active. Note: If Telnet is not installed, enable it using: dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
4. Use Windows Firewall to Check Open Ports
Windows Firewall can list all open and blocked ports.
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator. Hit the Winkey + R to open Run box, then Hit CTRL SHIFT AND ENTER on the keyboard to open as admin.
- Type:
netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name=all - Look for your blocked port in the list. If the rule appears, it is successfully blocked.
- You can also see the blocked port in the Windows Firewall as shown below.
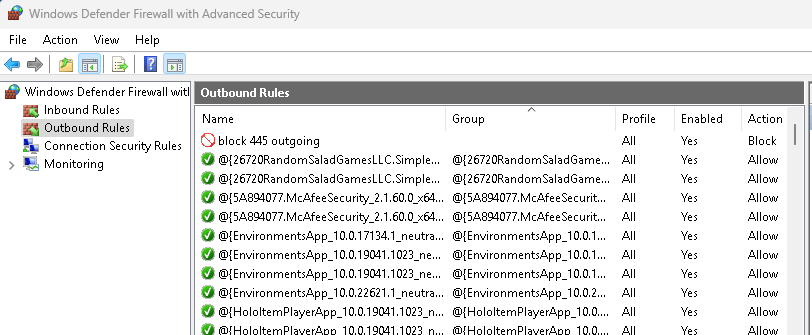
5. Use an Online Port Scanner (For External Testing)
To check if your internet-facing ports are blocked from outside, use an online port scanner like:
- GRC ShieldsUP! → https://www.grc.com/x/ne.dll?bh0bkyd2
- YouGetSignal → https://www.yougetsignal.com/tools/open-ports/
Steps:
- Visit the website.
- Enter your public IP address (or let it auto-detect).
- Enter the port number to scan.
- Click Check.
If blocked, it will show “Closed” or “Stealth”.
If open, it will show “Open”, meaning the port is still accessible.
6. Use Nmap to Scan Your Ports
Nmap is a powerful network scanning tool that can check which ports are open.
Steps:
- Download Nmap from https://nmap.org/download.html.
- Open Command Prompt.
- Run the following scan:
nmap -p [PORT] localhostExample (Checking Port 445):nmap -p 445 localhost- If blocked, it will show “filtered” or “closed”.
If open, it will show “open”.
- If blocked, it will show “filtered” or “closed”.
To scan all ports:
nmap -p- localhost
7 .Test Firewall Rules for a Specific Port
To check if Windows Firewall is blocking a port, use this command:
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type:
netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Block Port [PORT]"Replace[PORT]with the blocked port number. Example (Checking if Port 445 is blocked):netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Block Port 445"- If the rule exists, the port is blocked.
If it says “No rules match the specified criteria”, then it’s not blocked.
- If the rule exists, the port is blocked.
Final Thoughts
Disabling unused ports improves security by reducing the attack surface.
Most users don’t need ports 135, 137-139, 445, 23, 3389, 20-21, or 5000 open.
Use a VPN and strong firewall rules for remote access instead of exposing ports.


